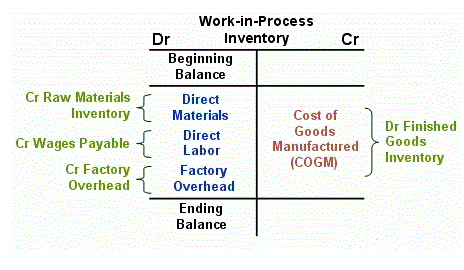
No concomitant care provided by anyone outside the trial team will be prohibited. Wherever possible, we will document these other forms of interventions to allow for sensitivity analysis if needed. All consent procedures with patients will be implemented by trained case managers, adhering to standard ethical guidelines. They will be responsible for screening of patients visiting the health centre to identify individuals with depression (the primary implementation outcome). They will also be responsible for scheduling the first HAP session, managing the counsellors’ case load, and referring patients to existing services based on a pre-defined protocol (Table 1). In India, the District Mental Health Program (DMHP) was started in 1996 under the Indian National Mental Health Program (NMHP) to decentralise mental health services by integrating them in general health care delivery and at the community level.

Additional consent provisions for collection and use of participant data and biological specimens 26b
- The management must look at the additional cost of producing the products under one roof.
- Marginal cost is the additional cost a company incurs when it produces one additional unit of output.
- The attempt to calculate and accurately predict such costs assist a company in making future investment decisions that can increase revenue and reduce costs.
- On the other hand, when incremental expenses exceed incremental revenues and a loss is incurred, an unprofitable situation results.
The coordinator will share the information only with those members of the team who would naturally remain unblinded because of the nature of their role (e.g. Sangathi facilitators). We will discontinue treatment in participants who (a) report any serious adverse events (SAE) deemed possibly caused by the trial interventions and (b) refuse treatment after consenting. Participants who develop serious suicidal ideation or risk of suicidal behaviour will receive supported referral to the DMHP to supplement the HAP. Additionally, participants who do not respond to the treatment at the end of eight sessions of HAP will also receive a referral to the DMHP. All these participants will be contacted for the outcome assessments, unless they withdraw their consent for follow-up. Table 1 summarises the various individuals involved in delivering, supporting, and supervising the interventions in the trial.
Understanding Incremental Analysis
Striking the right balance between overproduction and underproduction ensures efficient resource incremental cost meaning utilization. Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.

Composition of the coordinating centre and trial steering committee 5d
Goods or services with high marginal costs tend to be unique and labor-intensive, whereas low marginal cost items are usually very price competitive. Incremental cost is choice-based; hence, it only includes forward-looking costs. The cost of building a factory and set-up costs for the plant are regarded https://www.bookstime.com/articles/how-an-accountant-can-help-your-business as sunk costs and are not included in the incremental cost calculation. Incremental cost is the total cost incurred due to an additional unit of product being produced. The primary analyses will compare the proportion of individuals identified with depression through screening in the health centres.
- Furthermore, coverage of minimally adequate treatment (i.e. treatment levels deemed minimally sufficient for common mental health problems) is lower still, from 23% in high-income countries to 3% in LMICs [4].
- A long run incremental cost (LRIC) refers to the changing costs that a company can somewhat foresee.
- This is because fixed costs are not relevant to the decision of whether or not to pursue a new project or venture.
- There is no guarantee that long run incremental costs will change in the exact amount predicted, but attempting to calculate such costs helps a company make future investment decisions.
- It ranges from 33% in high-income countries to 8% in low- and lower middle-income countries (LMICs) [4].
- Profitable business decisions include knowing when is the best opportunity to produce more goods and sell at a lower price.
Participant timeline 13 (Table
The marginal cost of capital is the additional cost a company incurs when it finances an additional project. This means the cost of production to make one shirt is at $10 in your normal production capacity. This way, companies develop a realistic production roadmap, with an exact number of goods to be produced and the pricing per unit, to achieve profit goals in a business quarter.
Trial design 8
In doing so, IMPRESS will address one of the major unanswered challenges in global mental health, i.e. the methods, acceptability, effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness of integrated community and primary care-based approaches to reduce the treatment gap for depression. Although depression is the leading cause of disability worldwide, treatment coverage for the condition is inadequate. Supply-side barriers (e.g. shortage of specialist mental health professionals) and demand-side barriers (e.g. lack of awareness about depression) lead to limited availability of evidence-based interventions, poor demand for care, and low levels of adherence to care. Incremental cost is calculated by analyzing the additional expenses involved in the production process, such as raw materials, for one additional unit of production. Understanding incremental costs can help companies boost production efficiency and profitability. Considering the limited resources allocated to mental healthcare even in high-income countries and the high costs of specialist human resource in such countries, one would expect such interventions to potentially have applicability even in these countries.
- Incremental and marginal costs are two fundamental tools to evaluate future production and investment opportunities.
- Although a portion of fixed costs can increase as production increases, the cost per unit usually declines since the company isn’t buying additional equipment or fixed costs to produce the added volume.
- Consent for the publication of study findings will be obtained from all participants before enrolment in the trial.
- Each study participant will receive a unique identification number to which all their trial data will be linked.
- It encompasses a broad spectrum, including the initial investment in new facilities and production lines, hiring more staff, purchasing additional supplies, and other overhead expenses.

Provisions for post-trial care 30